- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
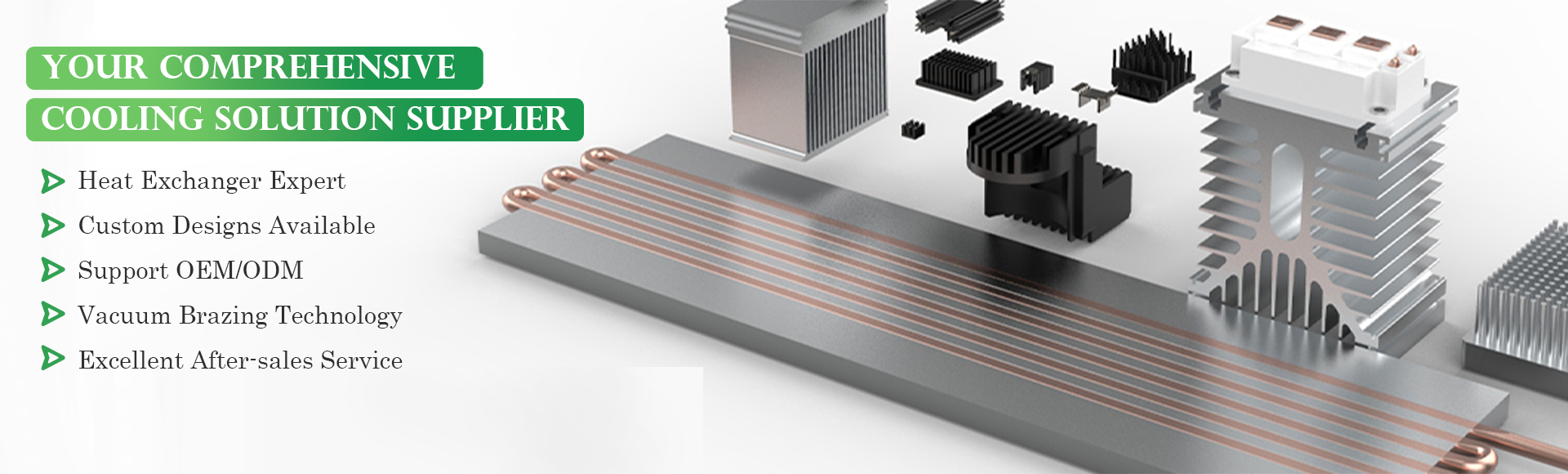


Product name :copper heat pipe heat sink with phase change material
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION | ||
NO. | ITEM | DESCRIPTION |
1 | Material | Aluminum alloy 6000 series and copper pipe |
2 | Section Dimension (W*H) | Up to 500*120 mm |
3 | Fin thickness | 0.2 to 1 mm |
4 | Fin spacing | Minimum 0.5 mm |
5 | Cooling Capacity | Up to 1200 W |
6 | Flatness for mounting surface | 0.15 mm |
7 | Surface roughness for mounting | 3.2 um |
8 | Manufacturing Method | CNC machining, extrusion and press |
9 | Cooling Method | Phase change |
10 | Surface Finish | Mill finish |
11 | Warranty time | 1 year |
12 | Place of Region | Jiangsu province of China |
13 | Reference Standard | GB/T 3190-2008,ISO 2768 |
M-stirling's heat sink technologies include
◆ CNC machined aluminum fins heat sink
◆ Skived aluminum heat sink
◆ Vacuum brazed bonded aluminum fins heat sink
◆ Extruded aluminum heat sink
◆ Die casting aluminum heat sink
◆ Epoxy glued bonded aluminum fin heat sink

▲ Copper heat sink
M-stirling's manufacture a wide range of heat sink include
● Cpu gpu ram heat sink
● Led aluminum heat sink
● Heat sink aluminum enclosure
● Copper heat pipe heat sink
● Liquid water cooling heat sink
● Inverter Aluminum Heatsink
● Other custom heat sinks

▲ Skived aluminum heat sink with copper heat pipe
Brief of heat sink
A heat sink (also commonly spelled heatsink) is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant, where it is dissipated away from the device, thereby allowing regulation of the device's temperature. In computers, heat sinks are used to cool CPUs, GPUs, and some chipsets and RAM modules. Heat sinks are used with high-power semiconductor devices such as power transistors and optoelectronics such as lasers and light-emitting diodes (LEDs), where the heat dissipation ability of the component itself is insufficient to moderate its temperature.
A heat sink is designed to maximize its surface area in contact with the cooling medium surrounding it, such as the air. Air velocity, choice of material, protrusion design and surface treatment are factors that affect the performance of a heat sink. Heat sink attachment methods and thermal interface materials also affect the die temperature of the integrated circuit. Thermal adhesive or thermal paste improve the heat sink's performance by filling air gaps between the heat sink and the heat spreader on the device. A heat sink is usually made out of aluminum or copper.
Product name :copper heat pipe heat sink with phase change material
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION | ||
NO. | ITEM | DESCRIPTION |
1 | Material | Aluminum alloy 6000 series and copper pipe |
2 | Section Dimension (W*H) | Up to 500*120 mm |
3 | Fin thickness | 0.2 to 1 mm |
4 | Fin spacing | Minimum 0.5 mm |
5 | Cooling Capacity | Up to 1200 W |
6 | Flatness for mounting surface | 0.15 mm |
7 | Surface roughness for mounting | 3.2 um |
8 | Manufacturing Method | CNC machining, extrusion and press |
9 | Cooling Method | Phase change |
10 | Surface Finish | Mill finish |
11 | Warranty time | 1 year |
12 | Place of Region | Jiangsu province of China |
13 | Reference Standard | GB/T 3190-2008,ISO 2768 |
M-stirling's heat sink technologies include
◆ CNC machined aluminum fins heat sink
◆ Skived aluminum heat sink
◆ Vacuum brazed bonded aluminum fins heat sink
◆ Extruded aluminum heat sink
◆ Die casting aluminum heat sink
◆ Epoxy glued bonded aluminum fin heat sink

▲ Copper heat sink
M-stirling's manufacture a wide range of heat sink include
● Cpu gpu ram heat sink
● Led aluminum heat sink
● Heat sink aluminum enclosure
● Copper heat pipe heat sink
● Liquid water cooling heat sink
● Inverter Aluminum Heatsink
● Other custom heat sinks

▲ Skived aluminum heat sink with copper heat pipe
Brief of heat sink
A heat sink (also commonly spelled heatsink) is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant, where it is dissipated away from the device, thereby allowing regulation of the device's temperature. In computers, heat sinks are used to cool CPUs, GPUs, and some chipsets and RAM modules. Heat sinks are used with high-power semiconductor devices such as power transistors and optoelectronics such as lasers and light-emitting diodes (LEDs), where the heat dissipation ability of the component itself is insufficient to moderate its temperature.
A heat sink is designed to maximize its surface area in contact with the cooling medium surrounding it, such as the air. Air velocity, choice of material, protrusion design and surface treatment are factors that affect the performance of a heat sink. Heat sink attachment methods and thermal interface materials also affect the die temperature of the integrated circuit. Thermal adhesive or thermal paste improve the heat sink's performance by filling air gaps between the heat sink and the heat spreader on the device. A heat sink is usually made out of aluminum or copper.

