- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search


| Availability: | |
|---|---|
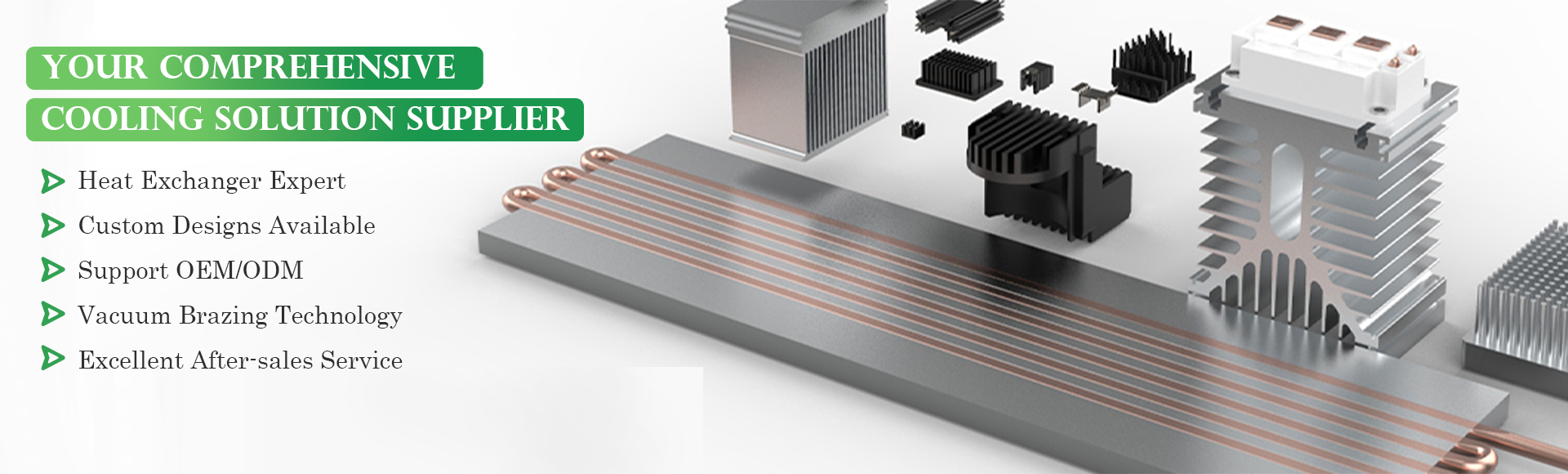
Product Name : Cooling Block For Pcb Copper Cold Plate cold plate with tube
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION | ||
NO. | ITEM | DESCRIPTION |
1 | Material for base | Aluminum alloy 3003, 6063,6061 |
2 | Material for tube | T2 pure copper |
3 | Tube Size | Φ9.52*0.7,10*1,10*1.5,12*1,12*1.5,12.7*0.7,14*1,16*1 mm |
4 | Dimension (L*W*T) | 600*500*15 mm |
5 | Cooling Capacity | 1 KW |
6 | Working Pressure | 3 to 4 bars |
7 | Flatness | 0.15 mm |
6 | Surface roughness | 3.2 um |
7 | Flow rate | 6 to 10 L/min |
8 | Manufacturing Method | CNC machining, rolling tube, pressing and glue sealing |
9 | Joining Method | Press lock and glue sealing |
10 | Cooling Method | Liquid cooling |
11 | Surface Finish | Mill finish or anodization |
12 | Coolant | Deionized Water,Inhibited Glycol and Water,Dielectric fluid |
13 | Warranty time | 1 year |
14 | Place of Region | Jiangsu province of China |
15 | Reference Standard | GB/T 3190-2008,GB/T 14846-2008,ISO 2768 |


Mstirling’s cold plate technologies include
◆ Vacuum brazed or controlled atmosphere brazed and CNC machined performance fin cold plates and chassis
◆ Friction Stir Welded (FSW) performance-fin cold plates and chassis
◆ flat tube cold plates
◆ Press lock Copper tubed cold plates
◆ Vacuum brazed and CNC machined copper cold plates
◆ Stamped and vacuum brazed cold plates
◆ Gun-drilled custom cold plate
◆ Custom channeled cold plate with ladder configuration
◆ Inner-Finned Brazed Cold Plates
◆ Aluminum extruded and welded or brazed cold plate
◆ Aluminum die casting and welded or brazed cold plate

▲ Components for vacuum brazed cold plate

▲ Stamped and vacuum brazed cold plate

▲ Copper tubed cold plate
We also supply value added components as below
● Fittings and connectors
● Hoses and tubes
● Heat exchangers or radiators
● Pumps and reservoirs
● Fans
● Other accessories

▲ Radiator ▲ Pump
Breif of Cold Plate Technologies
Performance requirements generally dictate choice of cold plate technology and design, and cold plate technology will drive cold plate cost. Generally, the cold plate's cost will increase with improving performance. Cold plate technologies include Press-Lock tubed, gun-drilled with or without expanded tubes, channeled, and brazed with internal fin. These technologies are listed in order of what is typically increasing cold plate efficiency and cost:
· Press-Lock Tubed Cold Plates - Press-Lock™ tubed cold plates have copper or stainless steel tubes pressed into a channeled aluminum extrusion. Custom tubed cold plates can be designed in virtually any shape or size and the fluid path can be custom designed for optimal thermal performance. Custom coatings, machining, drilling, and tapping may be incorporated as well.
· Gun-Drilled Cold Plates - Gun-drilled cold plates are fabricated by drilling a hole through an aluminum plate, and, when applicable, inserting and expanding copper or stainless steel tubing. This results in dual-sided cold plates that can be drilled or tapped. One additional benefit of gun-drilled cold plates is that they can have tighter tolerances than tubed cold plates, specifically for flatness requirements.
· Channeled Cold Plates - Channeled cold plates are extrusions with multi-channels, machined channels, or other methods of forming channels. The extrusions can provide only straight channels, but machining and other new metal cutting methods can provide a much more efficient shape. Channeled cold plates can be manufactured in any length, and assembled in a ladder configuration or integrated into a base plate for large area cooling. They can also be conversion coated or anodized for added protection. Several patterns for different ranges of required impedance, pressure drop, and flow have been developed.
· Inner-Finned Brazed Cold Plates - Inner-finned brazed cold plates consist of two plates metallurgically bonded together with internal fin. They can be vacuum-brazed with a variety of fin densities and shapes (plain, louvered, lanced-offset, etc.). This internal fin, such as the fin adds valuable heat transfer surface and adds turbulence to the flow. Brazed cold plates generally have the most flexibility with their design.
Product Name : Cooling Block For Pcb Copper Cold Plate cold plate with tube
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION | ||
NO. | ITEM | DESCRIPTION |
1 | Material for base | Aluminum alloy 3003, 6063,6061 |
2 | Material for tube | T2 pure copper |
3 | Tube Size | Φ9.52*0.7,10*1,10*1.5,12*1,12*1.5,12.7*0.7,14*1,16*1 mm |
4 | Dimension (L*W*T) | 600*500*15 mm |
5 | Cooling Capacity | 1 KW |
6 | Working Pressure | 3 to 4 bars |
7 | Flatness | 0.15 mm |
6 | Surface roughness | 3.2 um |
7 | Flow rate | 6 to 10 L/min |
8 | Manufacturing Method | CNC machining, rolling tube, pressing and glue sealing |
9 | Joining Method | Press lock and glue sealing |
10 | Cooling Method | Liquid cooling |
11 | Surface Finish | Mill finish or anodization |
12 | Coolant | Deionized Water,Inhibited Glycol and Water,Dielectric fluid |
13 | Warranty time | 1 year |
14 | Place of Region | Jiangsu province of China |
15 | Reference Standard | GB/T 3190-2008,GB/T 14846-2008,ISO 2768 |


Mstirling’s cold plate technologies include
◆ Vacuum brazed or controlled atmosphere brazed and CNC machined performance fin cold plates and chassis
◆ Friction Stir Welded (FSW) performance-fin cold plates and chassis
◆ flat tube cold plates
◆ Press lock Copper tubed cold plates
◆ Vacuum brazed and CNC machined copper cold plates
◆ Stamped and vacuum brazed cold plates
◆ Gun-drilled custom cold plate
◆ Custom channeled cold plate with ladder configuration
◆ Inner-Finned Brazed Cold Plates
◆ Aluminum extruded and welded or brazed cold plate
◆ Aluminum die casting and welded or brazed cold plate

▲ Components for vacuum brazed cold plate

▲ Stamped and vacuum brazed cold plate

▲ Copper tubed cold plate
We also supply value added components as below
● Fittings and connectors
● Hoses and tubes
● Heat exchangers or radiators
● Pumps and reservoirs
● Fans
● Other accessories

▲ Radiator ▲ Pump
Breif of Cold Plate Technologies
Performance requirements generally dictate choice of cold plate technology and design, and cold plate technology will drive cold plate cost. Generally, the cold plate's cost will increase with improving performance. Cold plate technologies include Press-Lock tubed, gun-drilled with or without expanded tubes, channeled, and brazed with internal fin. These technologies are listed in order of what is typically increasing cold plate efficiency and cost:
· Press-Lock Tubed Cold Plates - Press-Lock™ tubed cold plates have copper or stainless steel tubes pressed into a channeled aluminum extrusion. Custom tubed cold plates can be designed in virtually any shape or size and the fluid path can be custom designed for optimal thermal performance. Custom coatings, machining, drilling, and tapping may be incorporated as well.
· Gun-Drilled Cold Plates - Gun-drilled cold plates are fabricated by drilling a hole through an aluminum plate, and, when applicable, inserting and expanding copper or stainless steel tubing. This results in dual-sided cold plates that can be drilled or tapped. One additional benefit of gun-drilled cold plates is that they can have tighter tolerances than tubed cold plates, specifically for flatness requirements.
· Channeled Cold Plates - Channeled cold plates are extrusions with multi-channels, machined channels, or other methods of forming channels. The extrusions can provide only straight channels, but machining and other new metal cutting methods can provide a much more efficient shape. Channeled cold plates can be manufactured in any length, and assembled in a ladder configuration or integrated into a base plate for large area cooling. They can also be conversion coated or anodized for added protection. Several patterns for different ranges of required impedance, pressure drop, and flow have been developed.
· Inner-Finned Brazed Cold Plates - Inner-finned brazed cold plates consist of two plates metallurgically bonded together with internal fin. They can be vacuum-brazed with a variety of fin densities and shapes (plain, louvered, lanced-offset, etc.). This internal fin, such as the fin adds valuable heat transfer surface and adds turbulence to the flow. Brazed cold plates generally have the most flexibility with their design.

