- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search


| Availability: | |
|---|---|
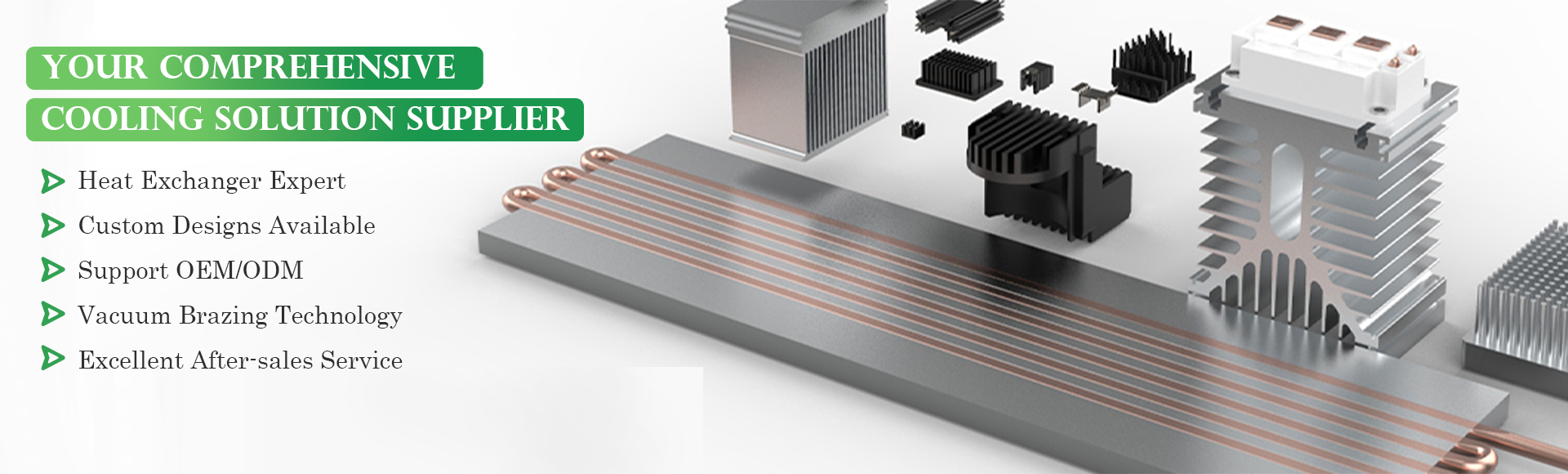
Product name : High-quality fan for better heat dissipation Aluminum Hydraulic Oil Cooled Cooling Radiator
The Heat Dissipation Oil Cooled Radiator is an advanced radiator designed to efficiently dissipate heat from industrial equipment and hydraulic systems. The core of the radiator is made up of a series of metal fins that are arranged in a grid-like pattern, providing maximum surface area for heat dissipation.
This radiator is specifically designed for use with oil-based systems, providing efficient heat dissipation and maintaining stable temperatures. Additionally, this Heat Dissipation Oil Cooled Radiator is designed to withstand harsh operating conditions, ensuring reliable performance and longevity.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION | ||
NO. | ITEM | DESCRIPTION |
1 | Material | Aluminum alloy |
2 | Dimension (L*W*T) | Up to 1200*1000*120 mm |
3 | Cooling Capacity | 300 to 2000 W |
4 | Working Pressure | 3 bars |
5 | Working temperature | 0 to 100℃ |
6 | Manufacturing Method | Brazing and welding |
7 | Cooling Method | Water to air |
9 | Surface Finish | Powder coating |
10 | Coolant | Deionized Water,Inhibited Glycol and Water,Dielectric fluid |
11 | Warranty time | 1 year |
12 | Place of Region | Jiangsu province of China |
13 | Reference Standard | GB/T 3190-2008,GB/T 14846-2008,ISO 2768 |
M-stirling’s radiators include
◆ Auto car radiators
◆ PC computer cooling radiators
◆ Motorcycle or electrical bicycle cooling radiators
◆ Vacuum or CAB brazed aluminum intercooler with aluminum extruded tanks welded



About radiator
Radiators are heat exchangers used to transfer thermal energy from one medium to another for the purpose of cooling and heating. The majority of radiators are constructed to function in cars, buildings, and electronics.
A radiator is always a source of heat to its environment, although this may be for either the purpose of heating this environment, or for cooling the fluid or coolant supplied to it, as for automotive engine cooling and HVAC dry cooling towers. Despite the name, most radiators transfer the bulk of their heat via convection instead of thermal radiation.
Product name : High-quality fan for better heat dissipation Aluminum Hydraulic Oil Cooled Cooling Radiator
The Heat Dissipation Oil Cooled Radiator is an advanced radiator designed to efficiently dissipate heat from industrial equipment and hydraulic systems. The core of the radiator is made up of a series of metal fins that are arranged in a grid-like pattern, providing maximum surface area for heat dissipation.
This radiator is specifically designed for use with oil-based systems, providing efficient heat dissipation and maintaining stable temperatures. Additionally, this Heat Dissipation Oil Cooled Radiator is designed to withstand harsh operating conditions, ensuring reliable performance and longevity.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION | ||
NO. | ITEM | DESCRIPTION |
1 | Material | Aluminum alloy |
2 | Dimension (L*W*T) | Up to 1200*1000*120 mm |
3 | Cooling Capacity | 300 to 2000 W |
4 | Working Pressure | 3 bars |
5 | Working temperature | 0 to 100℃ |
6 | Manufacturing Method | Brazing and welding |
7 | Cooling Method | Water to air |
9 | Surface Finish | Powder coating |
10 | Coolant | Deionized Water,Inhibited Glycol and Water,Dielectric fluid |
11 | Warranty time | 1 year |
12 | Place of Region | Jiangsu province of China |
13 | Reference Standard | GB/T 3190-2008,GB/T 14846-2008,ISO 2768 |
M-stirling’s radiators include
◆ Auto car radiators
◆ PC computer cooling radiators
◆ Motorcycle or electrical bicycle cooling radiators
◆ Vacuum or CAB brazed aluminum intercooler with aluminum extruded tanks welded



About radiator
Radiators are heat exchangers used to transfer thermal energy from one medium to another for the purpose of cooling and heating. The majority of radiators are constructed to function in cars, buildings, and electronics.
A radiator is always a source of heat to its environment, although this may be for either the purpose of heating this environment, or for cooling the fluid or coolant supplied to it, as for automotive engine cooling and HVAC dry cooling towers. Despite the name, most radiators transfer the bulk of their heat via convection instead of thermal radiation.

